Financial Ratio Analysis: Meaning, Types and Formula

As the expenses are used or expire, expense is increased and prepaid expense is decreased. Sales are reported in the accounting period in which title to the merchandise was transferred from the seller to the buyer. When inventory items are acquired or produced at varying costs, the company will need to make an assumption on how to flow the changing costs. A cost flow assumption where the last (recent) costs are assumed to flow out of the asset account first. To learn more about this important financial statement, visit our Cash Flow Statement Explanation. An additional column could be added to the worksheet to show the days’ sales in inventory (Ratio #13 which follows).
#14 – Days Payable Ratio Analysis

It is possible to distinguish six types of available financial ratios depending on the data type they contain. Using ratios in each category will be useful to fully understand the company’s operations across multiple fronts, as it will reveal likely problem areas. Ratio analysis can be used to evaluate the performance of the company in terms of profitability, liquidity, efficiency and solvency. It can also be used to cross-comparison between two companies, and forecast future performance. This ratio indicates the company’s ability to pay what is financial ratio analysis debts by comparing its total debt to its assets and how much debt is against the assets.
Cost to Income Ratio:
This report shows whether an organization has enough liquidity to sustain its operations in the short payroll term. Liquidity is the capacity of a business to find the resources needed to meet its obligations in the short term. By looking at the primary financial statements (Balance Sheet and Income Statement), you won’t be able to find an answer unless you ask the right questions.
Interest coverage ratio
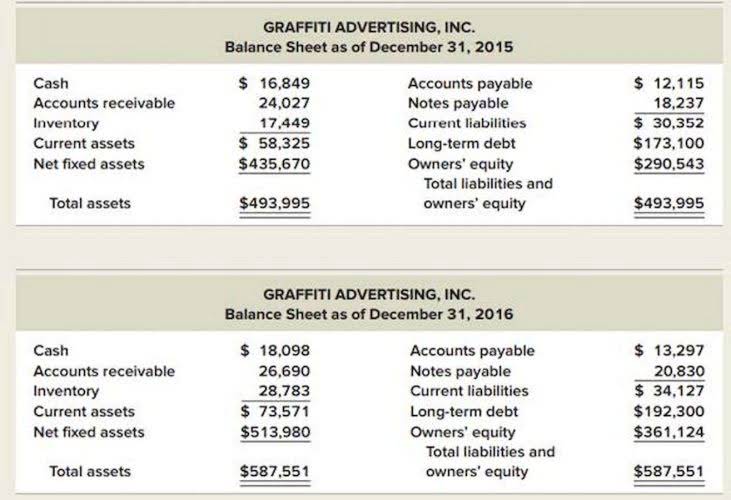
Understanding trends in key financial ratios is essential for a thorough fundamental analysis of public companies. The working capital turnover ratio measures a company’s ability to use working capital to generate sales. In the calculation, we divide the revenue figure by the average working capital. We can find the revenue numbers on the top row of the income statement. Meanwhile, for working capital, we calculate it by subtracting current assets from current liabilities.
For example, an industry facing disruption or consolidation requires a different strategy than a steadily growing industry. For example, suppose a Rs.100,000 investment is expected to produce Rs.20,000 in annual savings; the simple payback period would be five years. The NPV and IRR would depend on the estimated useful life, discount rate, and projected cash flows.
- Ratios provide them with a guide for drawing conclusions from the analysis they perform.
- This analysis defines how well a company performs compared to its competitors and the industry.
- In such situations, ratio analysis becomes a convenient tool that helps you easily understand the company’s performance based on some ratios.
- When, instead, the debt grows (and interest expenses grow exponentially) too much this can be a real problem.
- ROCE helps determine how profitably a company utilizes its capital and compares profitability between companies.
The objectives of ratio analysis are to make accounting information easier to understand and to assess a company’s financial health. It helps determine liquidity, which is the ability of a company to meet its short-term financial obligations. Also, it assesses the solvency position of a company, which shows the company’s ability to meet both short-term and long-term financial commitments.
- Simply put, it tells you how the company is utilizing its resources to generate profits.
- Loans to Deposits Ratio (LDR) or Credit to Deposit Ratio (CDR) ratio is typically used to assess a bank’s liquidity by comparing its loans to its deposits.
- Risk analysis examines the uncertainty of income for the firm and for an investor.
- Ratios generally are not useful unless they are benchmarked against something else, like past performance or another company.
- Lenders may set specific financial ratio requirements as part of loan covenants in the terms and conditions.
- For example, comparing profit margins, return on equity, and revenue growth reveals which companies are most efficiently converting business activities into profits.
#34 – Sustainable Growth
Accounts payable turnover shows us how well the company utilizes credit facilities from its suppliers. These formulas provide insights into different aspects of a company’s financial performance and are essential for decision-making. Ratio analysis is a powerful tool that helps in performing a fundamental analysis of a company. It helps investors know about the financial performance of a company which is key to making smart investment decisions. Financial ratio analysis is one of the most important techniques that stakeholders employ to evaluate the financial novelties, technical performance and market reputation of any organization.
This ratio shows us whether the company’s current assets are sufficient to pay its short-term liabilities. A current ratio value equal to 1 is usually a limit, which means current assets are equal to current liabilities. If it is less than one, it can mean the company has a liquidity problem. Companies often establish internal targets for their financial ratios, aiming to either maintain current performance levels or drive operational growth.
Analyzing past and current ratios provides a basis for making educated guesses about a company’s future prospects. For example, an increasing accounts receivable turnover ratio suggests a company expects rising sales and cash flow going forward. Ratio analysis enhances predictive ability and supplements other forecasting methods. Horizontal analysis provides a critical historical perspective when deciding whether to invest in a stock. Reviewing financial ratios like return on assets and profit margins over the past 5-10 years reveals positive https://squadra-eg.com/activity-based-costing-abc-a-detailed-definition/ or negative trajectories. These ratios indicate the company is likely able to meet its long-term obligations.

Cevapla
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!